Byte Insight: Did you know? Unlocking the Power of PySpark's Parallel Processing
Improve your data platform capabilities with PySpark processing
Since the beginning of the 2000s, there has been an influx of technologies that are able to produce and send data. According to an article by Exploding Topics over 402 million terabytes of data are generated PER DAY. Due to this huge amount of data, teams have had to come up with new ways of being able to store, transform and report on data from all sorts of devices.
How can we process mass amounts of data in an quick and cost efficient way? PySpark.
What is PySpark?
PySpark is the Python API for Apache Spark, an open-source distributed computing framework. Pyspark’s magic lies in its ability to process data in parallel across clusters of machines. Making it a top solution for data engineers and data professionals.
The funny thing is, did you know how easy it is to implement parallel processing with PySpark? I’ll break it down for you below.
Parallelism in Simple Terms
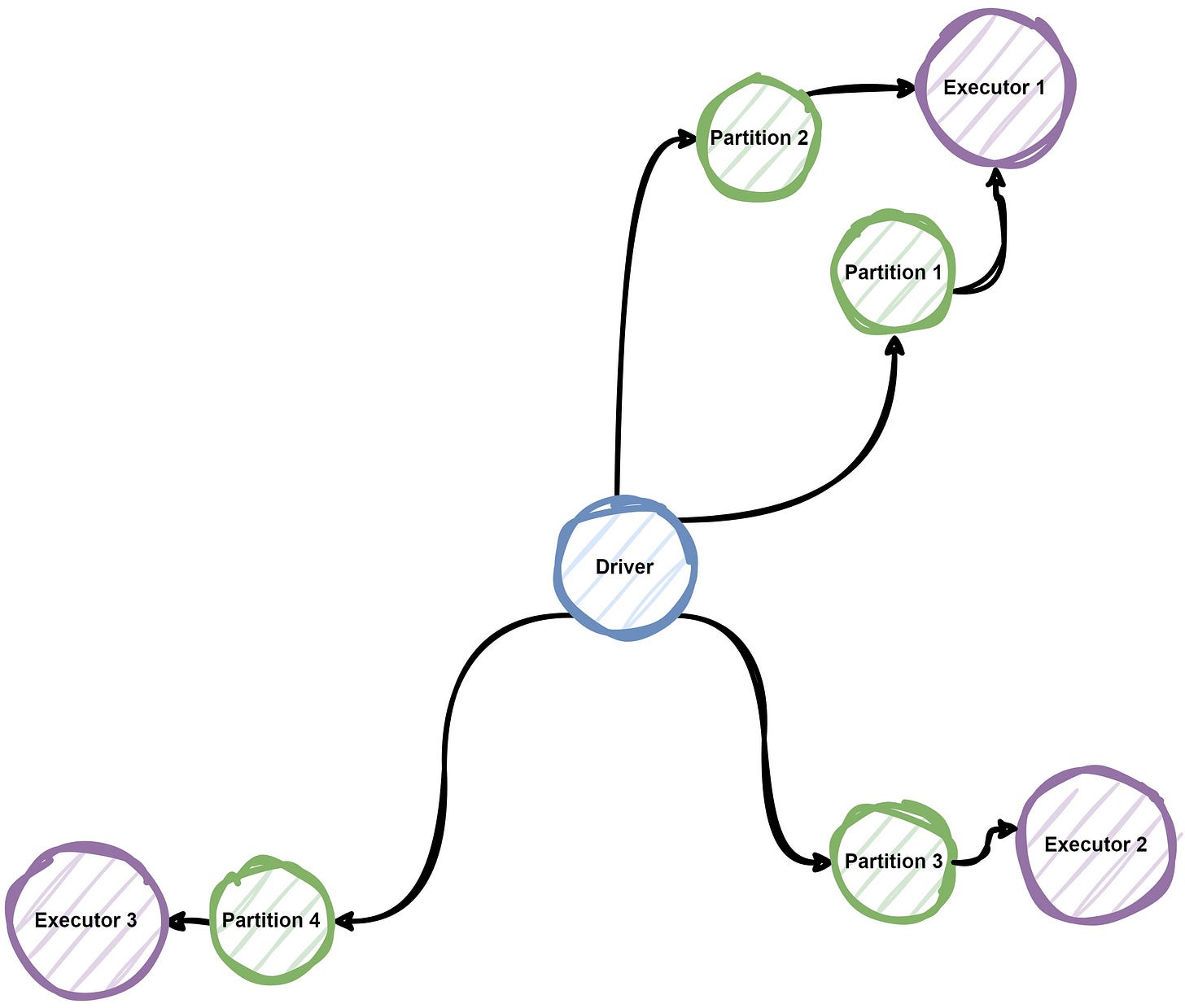
In PySpark, Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) and Data Frames are key to enabling parallelism.
RDDs: Low-level, flexible distributed data structures that allow transformations and actions across partitions.
Data Frames: Similar to SQL tables which optimise query execution using Sparks Catylst Optimiser. Vishal Barvaliya has a written a great post on how this works here.
In the background, Spark automatically distributes the data and computations across multiple nodes, dividing tasks into smaller units called partitions, Each partition in processed independently, enabling parallel execution.
PySpark in Motion
To see an example of how this works, lets take a classic word count to show PySpark capabilities:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Create a Spark session
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("WordCount").getOrCreate()
# Load a text file into an RDD
text_file = spark.sparkContext.textFile("<path to file")
# Perform the word count
tokenized = text_file.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" "))
word_counts = tokenized.map(lambda word: (word, 1)).reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)
# Collect the results
print(word_counts.collect())
# Stop the Spark session
spark.stop()So, let’s breakdown what happened when this script ran:
Data Partitioning - The text file is split into multiple partitions.
Task Assignment - Each partition is assigned to a node in the cluster
Parallel Execution - Tasks are executed independently and combined at the end
This parallelism allows Spark to process terabytes of data within seconds, something that would be impossible for standard python processing.
Tops Tips for Parallel Processing
Optimise your partitions: A general rule of thumb is having 2-4 partitions per CPU core. You can use the repartition() function to adjust partition sizes for optimal perfomance.
Leverage Broadcast Variables: When working with small lookup tables, use sc.broadcast to share data efficiently across nodes.
Avoid Shuffles: Minimise operations like join, groupByKey, or repartition that trigger expensive network shuffles. Use reduceByKey or mapPartitions for better performance.
Caching: Persist intermediate results using .cache() or .persist() to avoid recomputation.
Monitor with Spark UI: Keep an eye on the Spark Web UI for insights into task execution, partitioning, and shuffle operations
PySpark Beyond the Basics
While PySpark excels in parallelising operations on large datasets, its abilities don’t stop there. It supports integration with machine learning libraries (MLlib), graph processing (GraphX), and streaming data (Structured Streaming).
Whether you’re building a robust ETL pipeline, running machine learning algorithms, or analysing real-time streams, PySpark’s parallelism provides unmatched performance!
My Opinion
Parallel processing is a game-changer in big data analytics, and PySpark makes it accessible to Python developers. By leveraging distributed computing, you can process huge datasets faster and more efficiently than ever before.
So, the next time you’re staring at a massive dataset, remember that PySpark’s parallel processing power is just a few lines of code away. Give it a try and take the stress off your shoulders and onto your clusters! (Which should have minimal stress!)
Thanks for reading, let me know in the comments below if PySpark is something you already use and how you’ve utilised it!